Linux Commands: wc
wc stands for word count. It is used to display the number of lines, words, characters, and byte for a file or input received via pipe(|). the output shown above is explained below. 1 - Number of lines. 2 - Number of words 14 - Number of bytes The...
wc stands for word count. It is used to display the number of lines, words, characters, and byte for a file or input received via pipe(|).
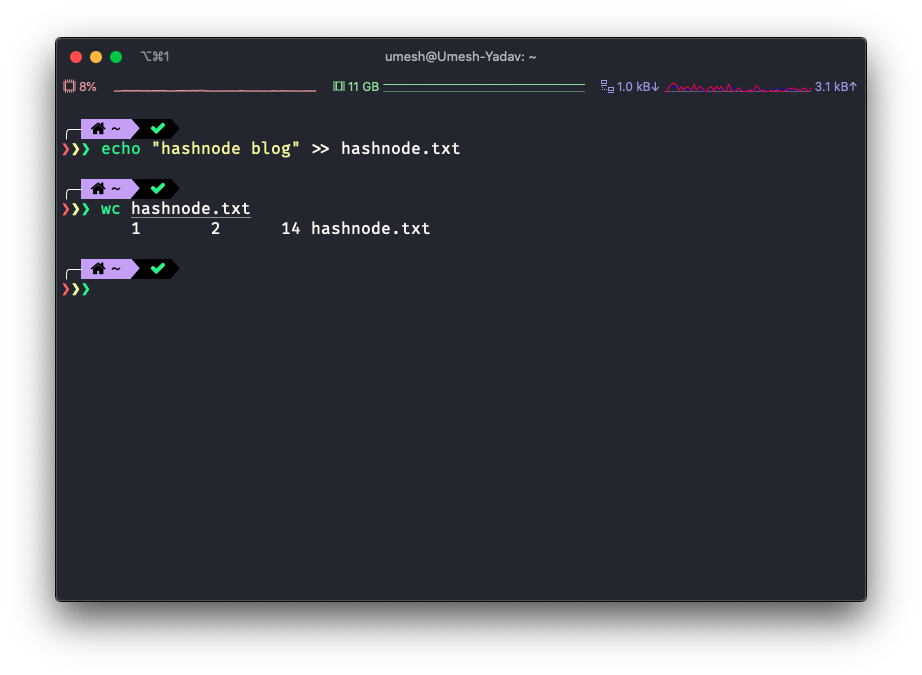
the output shown above is explained below.
- 1 - Number of lines.
- 2 - Number of words
- 14 - Number of bytes
There are four options that can be used with wc.
- -c: The number of bytes in each input file is written to the standard output.
- -l: The number of lines in each input file is written to the standard output.
- -m: The number of characters in each input file is written to the standard output. If the current locale does not support multi-byte characters, this is equivalent to the -c option.
- -w: The number of words in each input file is written to the standard output.
Let’s see these options in action.
This will count the lines.
$ wc -l hashnode.txt
1 hashnode.txtThis will count the words.
$ wc -w hashnode.txt
2 hashnode.txtThis will count the number of bytes.
$ wc -c hashnode.txt
14 hashnode.txtBut sometimes you have a file with multi-byte(non-ASCII charsets). For example, the Unicode character where one character is represented by multiple bytes.
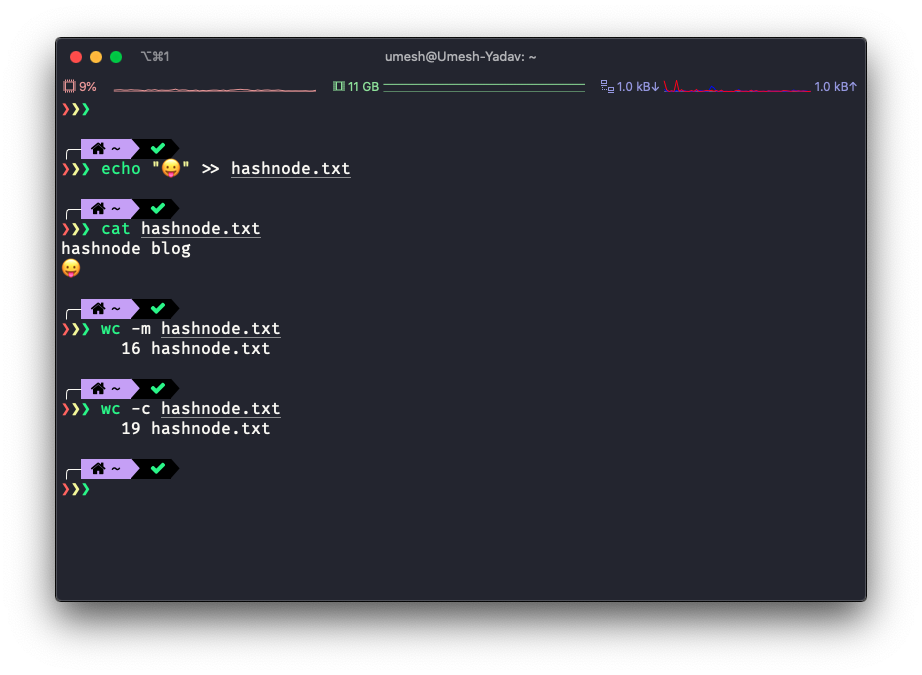
If you see this carefully, we added an emoji character to the end of the file. Both -c and -m output differ from each other because of that.
You can also pass more than one file to the wc as input.
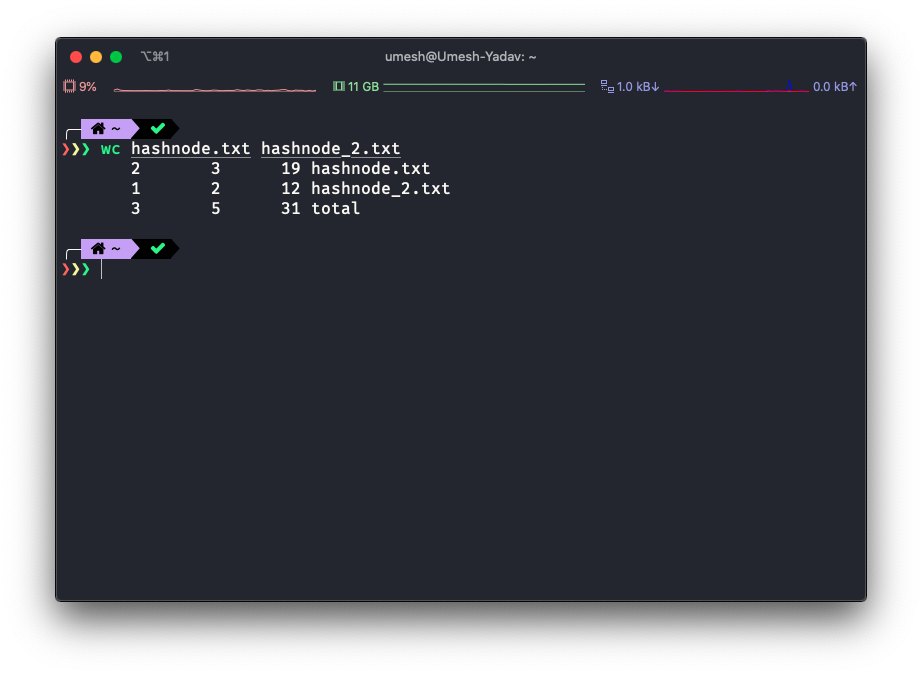
Advance usage.
You can also apply the wc on the output of other commands.
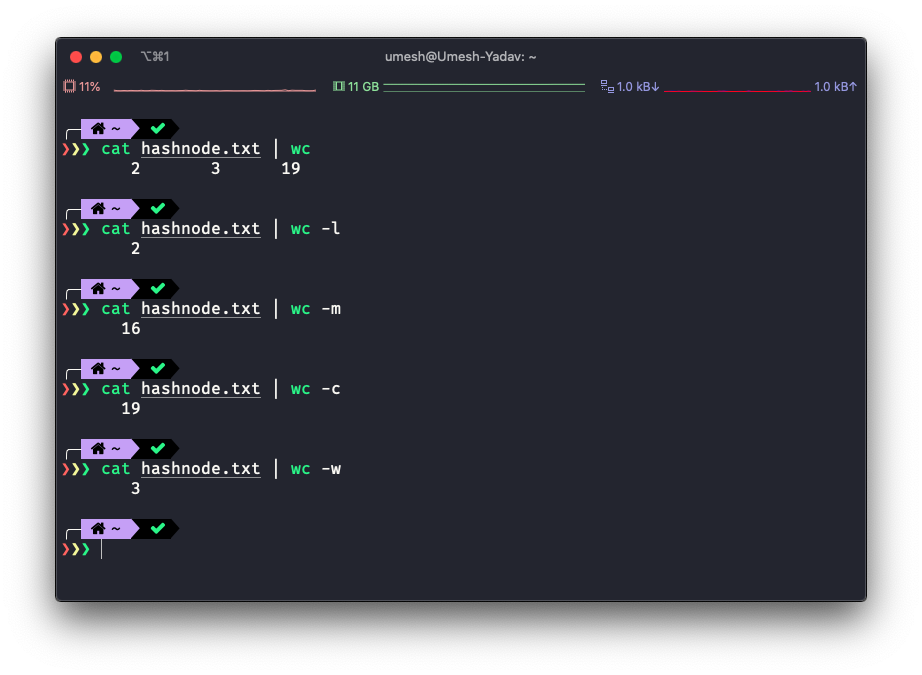
$ ls -al | wc
118 1065 7139Conclusion
wc is very helpful and can be used quite frequently.